Truth tables
Categories: logic logic gates
A truth table is a way of representing the output of a logic gate for every possible set of inputs.
2 input gates
We have already seen the example of a 2 input AND gate, which has a truth table like this:
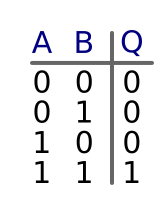
Since there are 2 inputs (A and B), and each input has 2 possible states (0 or 1), there are 4 possible combinations of inputs: (0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0) and (1, 1). In the case of an AND gate, the output is 0 unless both inputs are 1.
Notice that we arrange the combinations in a particular order. If you look down the columns:
- The values of B are 0, 1, 0, 1
- The values of A are 0, 0, 1, 1
3 input gates
It is possible for a gate to have more than 2 inputs. In the case of a gate with 3 inputs (A, B and C), there are 8 possible combinations (222). Here is the truth table for a 3 input and gate

In this case, the output is 0 unless all 3 inputs are 1.
Again, we arrange the combinations in a similar order. If you look down the columns:
- The values of C are 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1
- The values of B are 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1
- The values of A are 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1
Why do we use that particular order? You can think of the inputs as being numbers in binary:
- 000 binary is 0 denary
- 001 binary is 1 denary
- 010 binary is 2 denary
- 011 binary is 3 denary
- etc
So we are just placing the rows in numerical order.
More inputs
It is possible to have logic circuits with 4 or more inputs, and we can simply extend the truth table to account for this.
For example, if there are 4 inputs (A, B, C and D), there will be 16 lines in the table. Extend the sequence of inputs using the same pattern.
See also
Sign up to the Creative Coding Newletter
Join my newsletter to receive occasional emails when new content is added, using the form below:
Popular tags
555 timer abstract data type abstraction addition algorithm and gate array ascii ascii85 base32 base64 battery binary binary encoding binary search bit block cipher block padding byte canvas colour coming soon computer music condition cryptographic attacks cryptography decomposition decryption deduplication dictionary attack encryption file server flash memory hard drive hashing hexadecimal hmac html image insertion sort ip address key derivation lamp linear search list mac mac address mesh network message authentication code music nand gate network storage none nor gate not gate op-amp or gate pixel private key python quantisation queue raid ram relational operator resources rgb rom search sort sound synthesis ssd star network supercollider svg switch symmetric encryption truth table turtle graphics yenc