File servers
Categories: memory and storage storage
If you own a laptop or PC, you probably keep all your work and applications on the hard drive. In a business or school, it is often better to keep everyone's documents in the same place, on a file server.
What is a file server?
A file server is often a single PC on the same local area network (LAN) as the users. It will normally be a high performance PC with plenty of memory and (of course) a lot of disk space.
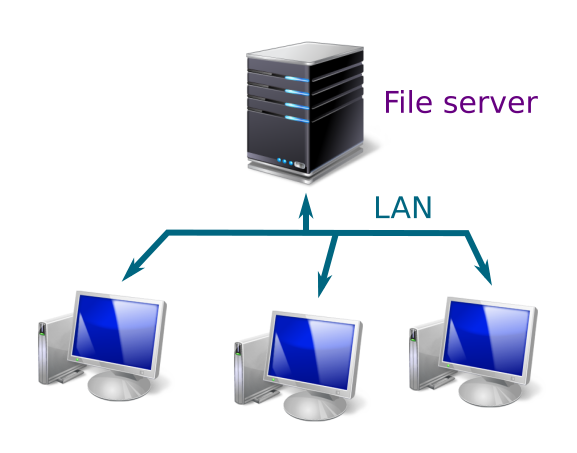
In larger offices with lots of users, a cluster of PCs might be used as the file server.
Users store all their work documents on the file server. Often, the computers in the office will access the file server as a shared disk drive. Commonly used applications might also be installed on the files server
Advantages of a file server
A file server lets you:
- share documents between people in the office.
- control which people can view or edit each document.
Having all the documents in one place helps to ensure that everything is backed up properly, and no important files are forgotten about. The server can be made more secure against cyber-attacks, for example by using a Linux PC.
If the server is used to store applications as well as documents, it means that new software versions can be installed in one place only.
Other functions of a file server
A file server is sometimes used to provide extra functionality:
- Automated backups - files can be backed up (to tape, or the cloud) regularly and automatically.
- Version control - the server can use software such as Git to track changes made to documents and files, recording who made changes, and allowing old versions to be retrieved if needed.
- Compression and deduplication (see below) - are used to save disk space.
File servers sometimes use a RAID filing system (see below) so they can continue working even if a disk drive fails.
A file server might sometimes also be used as a:
- print server - the file server is used to queue jobs waiting to be printed, and allow print jobs to be prioritised or cancelled while they are in the queue.
- mail server - stores incoming emails and keeps them until users view them in their email program.
Deduplication
Deduplication is a way of reducing the amount of disk space required to save files.
It works by spotting identical blocks of data, and only storing them on the disk once. Identical blocks often occur where the same file, or 2 slightly different versions of a file, are stored on disk.
On the file server, sometimes several users will store the same file, and deduplication avoids wasting space.
RAID
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (although some people say it stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks).
The basic idea of RAID is to combine 2 or more separate physical hard disks to behave as a single disk. RAID has two objectives:
Redundancy - some RAID systems write the same data to two disks. This means that if one disk fails, the system can continue working with the disk that still works. At some point, for example at the end of the working day, the faulty disk can be replaced.
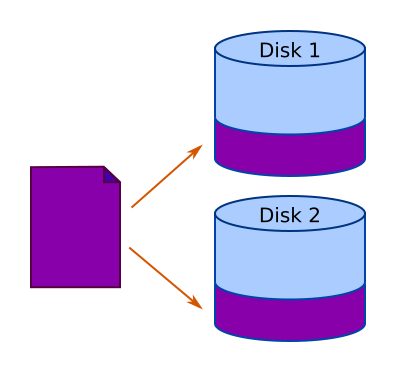
The advantage of this system is that even if one of the hard disks on the file server fails completely, the users won't even know - they can carry on as if nothing has happened.
RAID is not really intended to replace data backup. It allows the system to keep running if a single disk fails, but it won't protect you against a power surge damaging several disks, or a virus overwriting everything, or someone accidentally deleting an important file.
Speed - some RAID system aim to speed up disk access. Instead of writing a file to one disk, the RAID system splits the file into stripes, and writes alternate stripes to different disks. The result of this is that you will get both disks writing data at the same time (each disk writing a different part of the file). Since this is the slowest part of the operation, the RAID array will be faster than a single disk.
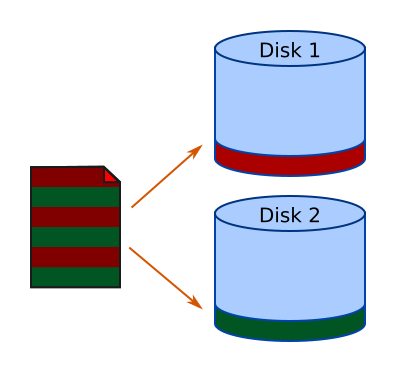
Some RAID systems attempt to provide increased speed and redundancy.
See also
Sign up to the Creative Coding Newletter
Join my newsletter to receive occasional emails when new content is added, using the form below:
Popular tags
555 timer abstract data type abstraction addition algorithm and gate array ascii ascii85 base32 base64 battery binary binary encoding binary search bit block cipher block padding byte canvas colour coming soon computer music condition cryptographic attacks cryptography decomposition decryption deduplication dictionary attack encryption file server flash memory hard drive hashing hexadecimal hmac html image insertion sort ip address key derivation lamp linear search list mac mac address mesh network message authentication code music nand gate network storage none nor gate not gate op-amp or gate pixel private key python quantisation queue raid ram relational operator resources rgb rom search sort sound synthesis ssd star network supercollider svg switch symmetric encryption truth table turtle graphics yenc